
Typically, the scale ranges from about 5 to 60 Btu/lbm (12 to 140 kJ/kg). It is typiĬally on the left, but sometimes on both sides, of the chart. This yields a dewpoint temperature of 60☏ (16☌).įigure 34-10 shows the enthalpy (h) scale.
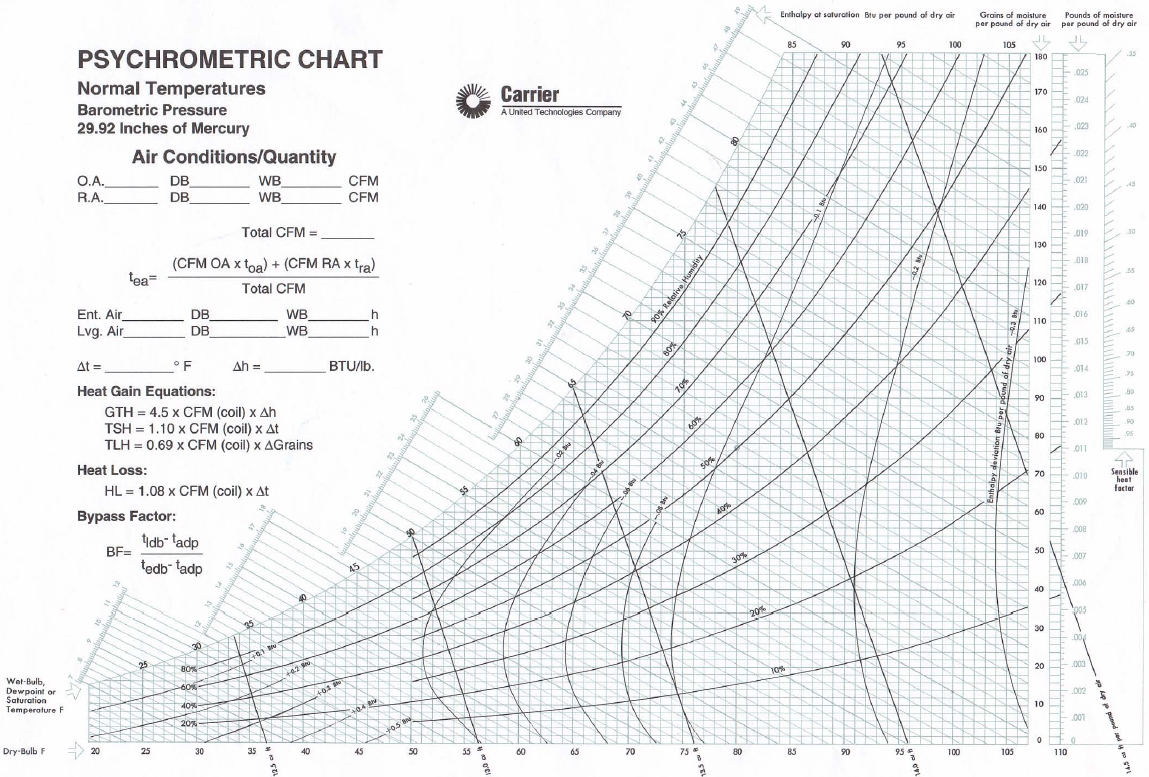
From this intersection, proceed horizontally to the saturation curve (100% RH). To determine the dewpoint temperature of air at 80☏ (27☌) and 50% RH, for example, start at the db temperature of 80☏ (27☌) and proceed vertically to the 50% RH curve. Dewpoint temperature lines run horizontally, like the grains of moisture lines, with a scale that typically ranges from 20 to 90☏ (-7 to 32☌). The scale, when included, is typically on the far right of the chart and the unit of measurement is in-Hg abs (cm-Hg abs or Pascal).įigure 34-9 shows the dewpoint temperature scale. This measures the pressure exerted by water vapor in the air. The difference is 90 grains (0.0128 kg/kg).įigure 34-8 shows the vapor pressure (Pv or Pw) scale. 34-8 Vapor Pressure Scale.įrom 90☏ (32☌) db to the 70% RH curve. For example, to determine the grains/lbm of dry air removed in conditioning air from 90☏ (32☌) and 70% RH to 80☏ (27☌) and 40% RH, proceed verticallyħ0CF Dry Bulb Fig. In SI unit charts, the corresponding scale is kg/kg of dry air and typically ranges from 0 to 0.033. The scale is in grains of moisture per lbm of dry air (grains/lbm) and typically ranges from 0 to about 200. These are shown as straight horizontal lines that are perpendicular to db lines. As RH decreases, the wb temperature becomes lower than the equivalent db temperature.įigure 34-7 shows specific humidity, or humidity ratio (w or HR), lines. At 100% RH, db temperature is equal to wb temperature. The RH lines are curved and the values appear in increments of 10%, representing the degree of saturation, or the ratio of the pressure of the vapor (pv) to the pressure of the vapor at saturation (pvs). In SI unit charts, the scale is in ☌.įigure 34-6 shows RH lines. 34-7 Specific Humidity (Humidity Ratio) Lines. 34-4 Sketch of Psychrometric Chart Highlighting One Specific Set of Conditions.įig. 34-2 Psychrometric Chart (English units). The scale called db temperature is laid out horizontally at the bottom of the chart in ☏, with the incremental lines extending Fig. These are shown as straight vertical lines. Each highlights particular scales and lines associated with each one of the seven conditions shown jointly in Figure 34-4.įigure 34-5 shows db temperature lines, i.e., the temperature of air measured on a standard thermometer.
CARRIER PSYCHROMETRIC CHART SI UNITS SERIES
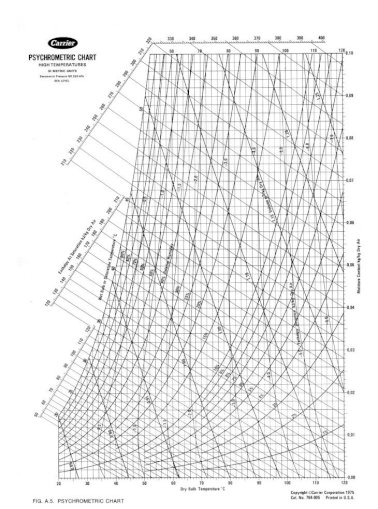
If any two properties of an air mixture are known, the chart allows a quick determination of all of its other properties.įollowing are a series of skeleton psychrometric charts. The darkened circle pinpoints the location of the specific condition and the intersecting horizontal and vertical lines show the scales from which the condition can be identified. Included are db and wb temperatures, RH, specific humidity, vapor pressure, dewpoint temperature, and enthalpy. Figure 34-3 is a psychrometric chart in SI units.įigure 34-4 is a basic sketch of a psychrometric chart the scales and lines of the chart are highlighted as they relate to one specific set of air conditions. The numbered lines or scales highlight the functionality of the chart. Figure 34-2 is a psychrometric chart in English units. The chart can be used to make calculations to determine the sensible and latent loads associated with HVAC equipment processes. It relates db temperature to absolute moisture content of the air and includes all of the possible combinations of temperature, moisture content, density, and heat content properties that can occur in air. It is essentially a graphic representation of the condition of air (air-water vapor mixture) at each point in the AC process. It graphically illustrates the relationship between db temperature, wb temperature, RH, humidity ratio, and enthalpy.
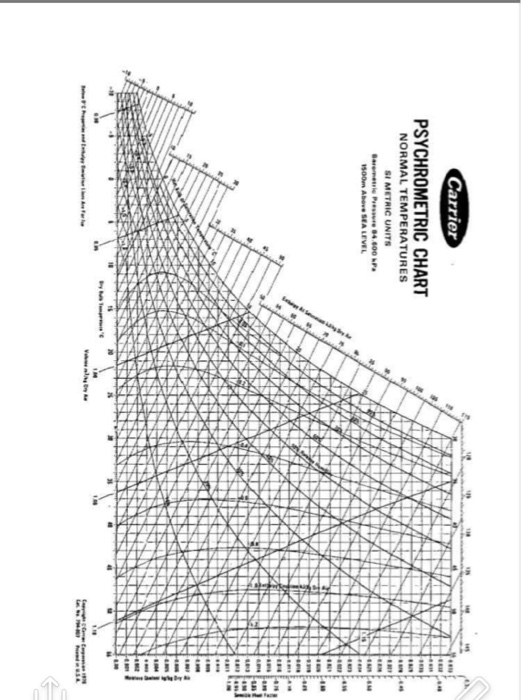
The psychrometric chart is a plot of the properties of atmospheric air.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
